Analyse the health of your parcel through biodiversity and pollution monitoring
Working together with wild bees and implementing an image recognition AI model, BeeOmetrics is a low cost nature-based solution which aims to provide detailed environmental measurements at site level (40 ha).

BeeOmetrics is an European Innovation Council-funded project

Purpose
What we’re aiming for
To protect and restore biodiversity, and reduce environmental pollution, our BeeOmetrics R&D project aims to introduce a cost-effective, non-intrusive green technology for environmental monitoring and remediation. It focuses on wild bees as a scalable environmental bioindicator.
Our solution will first make it possible to monitor specific pollution and biodiversity metrics, facilitating in-depth ecosystem health analysis, and through AI, will also generate predictive recommendations for remediating environmental contaminants and revitalizing biodiversity.
BeeOmetrics is designed to offer metrics and recommendations to policy makers, businesses and land managers, empowering them to make informed choices.
Mission
Project Timeline
& Practicalities
50 sites to be selected in 2024 in Belgium and France
Sites in both agricultural and urban settings
2 years of data collection: 2024, 2025
How it works
How does BeeOmetrics work?
The machine learning model that the BeeOmetrics platform will use to make estimations of ecosystem health indicators is based on measurements taken from three primary sources:
AI powered predictive platform, showing interpretation, KPIs & actions
- Indicators from air, ground, plants & wild pollinators
- Multi-factor & multi-indicator ecosys, health reports
- Recommendations for ecosys, health improvement
On-site plant samples
Plants biodiversity & pollen polluants
#eDNA, bioinformatics
#mass spec/chromato analysis
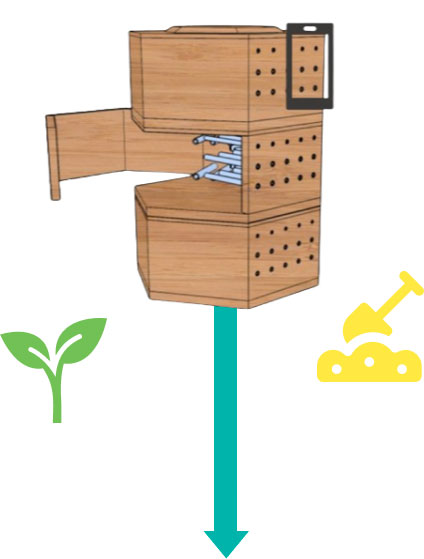
Picture of “Beeôtel” nests
Wild bee (40ha foraging area) biodiversity & population density
#AI, ML, image recognition
#participative science
Sensors
Air pollution, temperature & humidity
#remote sensors
Soil samples
Soil buidiversity & soil pollutants
#eDNA, bioinformatics
#mass spec/chromato analysis
Plant samples
Plant biodiversity
#eDNA, bioinformatics
On-site plant samples
Plants biodiversity & pollen polluants
#eDNA, bioinformatics
#mass spec/chromato analysis
Picture of “Beeôtel” nests
Wild bee (40ha foraging area) biodiversity & population density
#AI, ML, image recognition
#participative science
Sensors
Air pollution, temperature & humidity
#remote sensors
Soil samples
Soil buidiversity & soil pollutants
#eDNA, bioinformatics
#mass spec/chromato analysis
Plant samples
Plant biodiversity
#eDNA, bioinformatics

A On-site bee hotel device, the “BeeÔtel”
B On-site soil samples
C On-site plant samples
A The BeeÔtel

Solitary bees
- Pollen samples, which allows to assess the surrounding plant biodiversity and pollution by eDNA analysis and chemical analysis respectively.
- Pollinator biodiversity determined by the BeeÔtel occupancy rates that indirectly allows us to assess the health of the surrounding ecosystem.
As solitary bees reside in the BeeÔtel, they leave characteristic “plugs” in the orifices, allowing to distinguish the species occupying each opening. Leveraging this fact, we will use an image recognition algorithm (step 2) to determine (i) the occupancy rate and (ii) biodiversity of local wild bee populations. These two elements can be used as core bioindicators for the health of an ecosystem.

Integrated Sensors
B On-site soil samples
- Chemical analysis to detect pesticides and heavy metals in the ecosystem.
- Environmental DNA analysis to determine soil health.
C On-site plant samples
The third BeeOmetrics data source is on-site plant samples (Step 5) which can be subjected to eDNA analysis to assess the species present in the ecosystem, including invasive or remarkable plants.
About
About BeeOdiversity

How BeeOmetrics partners are helping protect pollinators and boost biodiversity
Discover how Crop’s and Earthworm Foundation contribute to BeeOmetrics, the EIC-funded project using wild bees to monitor environmental health across Europe.
Sharing BeeOmetrics with the world at Biomim’expo 2025
BeeOdiversity presented BeeOmetrics for the first time at Biomim’expo 2025 in Marseille. Discover how wild-bee-based biomonitoring, AI and science are helping measure biodiversity and pollution to support real regeneration on the ground.
Smarter BeeOtels: new IoT sensors to monitor ecosystem health
The BeeOmetrics team is buzzing with excitement: our BeeOtels just got a major upgrade with new IoT kits to supercharge their data collection capabilities.



